Tietopankki
Head types
Recesses (notches)
Thread end types
Material types
Protective coatings
Electrolytic zinc coatings
Chromate conversion coatings
Nickel coating
Brass plating
Phosphating
Oxidisation
List of standards
Head types
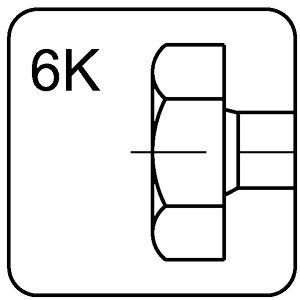 hexagonal head – 6K
hexagonal head – 6K
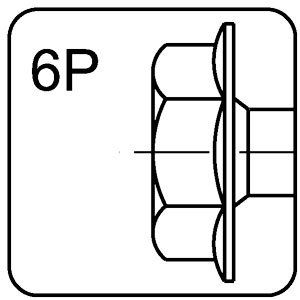 hexagonal head with washer – 6P
hexagonal head with washer – 6P
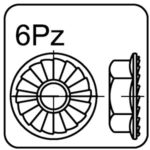 hexagon washer head with serration – 6Pz
hexagon washer head with serration – 6Pz
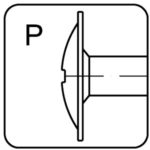 with washer – P
with washer – P
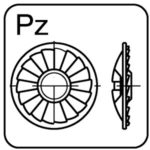 with serrated washer – Pz
with serrated washer – Pz
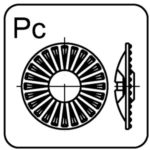 head with ribbed washer – Pc
head with ribbed washer – Pc
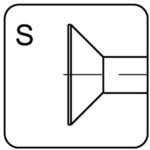 flat head – S
flat head – S
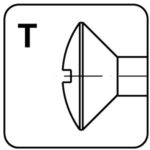 oval head – T
oval head – T
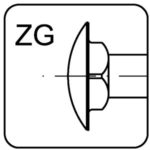 mushroom head with square neck – ZG
mushroom head with square neck – ZG
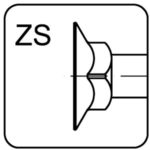 flat head with squere neck – ZS
flat head with squere neck – ZS
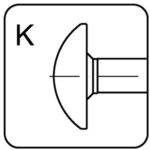 round – K
round – K
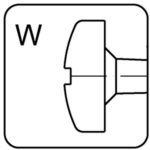
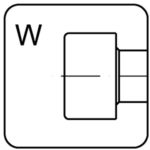
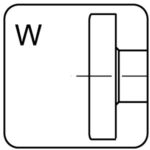 pan head – W
pan head – W
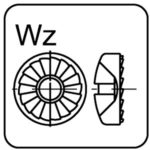 pan head, serrated – Wz
pan head, serrated – Wz
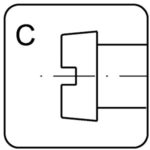 cylindrical – C
cylindrical – C
 square – 4K
square – 4K
 hexagon washer head – 6P*
hexagon washer head – 6P*
Recesses (notches)
 cross (Pozidriv) – PZ
cross (Pozidriv) – PZ
 cross (Philips) – PH
cross (Philips) – PH
 slotted – ZW
slotted – ZW
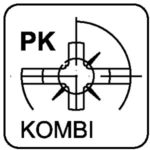 kombi (Pozidriv) – KOMBI
kombi (Pozidriv) – KOMBI
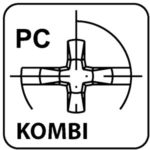 kombi (Phillips) – KOMBI
kombi (Phillips) – KOMBI
 hex socket – IM
hex socket – IM
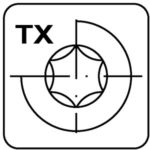 Torx – TX
Torx – TX
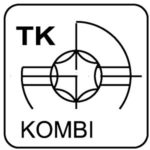 T-KOMBI torx – TK
T-KOMBI torx – TK
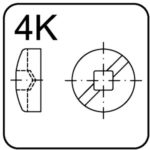 KOMBI (square) – 4K
KOMBI (square) – 4K
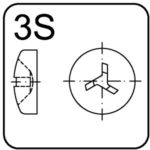 tri-wing – 3S
tri-wing – 3S
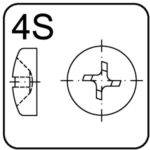 torgu-set
torgu-set
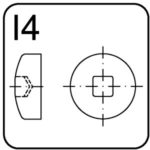 square – I4
square – I4
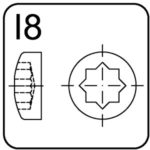 octagonal – I8
octagonal – I8
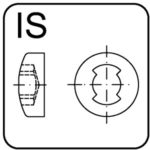 clutch – IS
clutch – IS
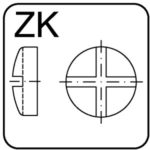 cross slotted – ZK
cross slotted – ZK
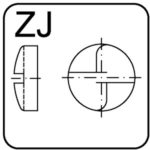 slotted one-way – ZJ
slotted one-way – ZJ
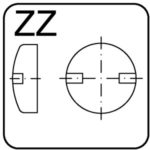 spanner slotted one-way – ZZ
spanner slotted one-way – ZZ
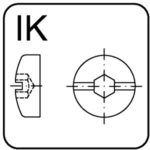 KOMBI hex socket – IK
KOMBI hex socket – IK
Thread end types
| Name | Symbol | Drawing examples | ||
| Screws with metric thread | Sheet metal screws | UNIX, for plastics | ||
| Cut |  |
 |
 |
 |
| With pilot | 
 |
     |
 |
 |
| Sharp |  |
 |
 |
 |
| With drill |  |
 |
||
| With drill and wings |  |
 |
||
Material types
 carbon steel
carbon steel
 hardened product
hardened product
 stainless steel
stainless steel
 acid-proof steel
acid-proof steel
 aluminium alloy
aluminium alloy
 aluminium alloy
aluminium alloy
 brass
brass
 copper
copper
 aluminum
aluminum
 EPDM rubber
EPDM rubber
 polyethylene
polyethylene
 polypropylene
polypropylene
 polyamide
polyamide
 PVC material (polyvinyl chloride)
PVC material (polyvinyl chloride)
Protective coatings
 zinc coating
zinc coating


 8µm, 12µm, 15µm zinc galvanic coating
8µm, 12µm, 15µm zinc galvanic coating
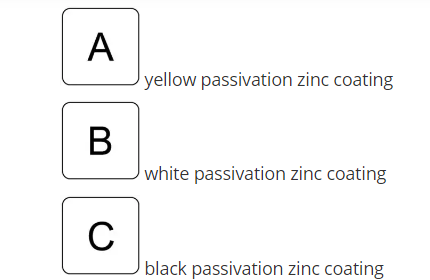
 yellow passivation zinc coating
yellow passivation zinc coating
 white passivation zinc coating
white passivation zinc coating
 black passivation zinc coating
black passivation zinc coating
 Zintec zinc coating – white
Zintec zinc coating – white
 silver-coloured ceramic coating
silver-coloured ceramic coating
 nickel coating
nickel coating
 brass-plated coating
brass-plated coating
 bluing
bluing
 phosphating
phosphating
 hot-dip galvanisation
hot-dip galvanisation
 Geomet
Geomet
 Zintec zinc coating – black
Zintec zinc coating – black
 Statuary Bronze Plated
Statuary Bronze Plated
Electrolytic zinc coatings
Electrolytic zinc coatings are commonly used protective coatings. The anti-corrosive properties of these coatings depend to a great extent on their thickness. The standard thickness of zinc coating we use during the production is 5pm. We also offer other thicknesses per Client’s request.
When choosing the thickness of the coating, you must take into account additional damaging factors, like: condensation of water vapour, the presence of damaging gases and vapours, the presence of electrolyte solutions, dust and sand.
The physical, chemical and mechanical properties of zinc coatings have an influence on products’
performance characteristics. These properties limit the use of coatings in the food industry and for
products requiring high hardness of the top coat. In such cases, zinc coatings are replaced with other,
adapted to specific working conditions.
In some cases, specially designed zinc coating technology allows for achieving protective and decorative effects that are especially recommended when high durability of the coating is not required.
Chromate conversion coatings
In order to increase corrosion protection, zinc coatings are conversion chromated (passivated). Conversion chromating also allows for achieving protective and decorative effects that are especially in cases where high abrasion durability of the coating is not required. For our products, we use a white, yellow and black coating.
Considering the colour of the obtained chromate coatings, it has to be stated that golden-yellow coatings exhibit significantly higher corrosion resistance than clear, colourless coatings.
Chromate coatings have relatively low abrasion resistance. This is especially true for thicker, black coatings. After drying, the abrasion resistance increases. Least susceptible to abrasion are colourless and white coatings.
Nickel coating
Electrolytic nickel coatings are used in engineering for decorative and protective purposes and as technical coatings. For our products, we use decorative and protective coatings which provide optimal protection against corrosion and high aesthetic qualities.
Nickel coatings are used for fasteners are characterised by high resistance to atmospheric corrosion. We offer two types of coatings: – matte for components like euro screws (screws for furniture fittings), – glossy for components like hinges, furniture joints.

Brass plating
Brasses are copper and zinc alloys. The properties of electrolytic brass-plated coatings vary, depending on the content of the main alloying element, which is zinc. The chemical composition of the coating has also a determining influence on its colour, which varies from red (high copper content) to different shades of gold-yellow. The standard type of brass-plated coatings is yellow.
They are characterised by high aesthetic qualities and protect against corrosion. The anti-corrosion properties of brass-plated coatings allow for use in slightly damaging environments. Years-long analysis of the properties and applications of brass-plated coatings have shown their high rated use in products like ERICSSON nuts.

Phosphating
Standard phosphate coatings on the fixing elements are mat of dark gray to black colour. Typical phosphate coatings on fasteners are matte, with colours ranging from dark grey to black. Phosphate coatings have anti-corrosion properties and additionally increase the adhesion of applied paint coatings. Phosphating is performed for drywall screws (coarse and fine thread, self-drilling).
The specific use of these products excludes the use of zinc coatings which are easily damaged by contact with gypsum. Phosphate coatings not only protect products against corrosion but also reduce friction coefficient and make installation easier.
Oxidisation
Bluing belongs to the group of conversion oxide coatings on steel. These coatings are made of iron oxides. Both the coating structure and its anti-corrosive properties vary, depending on its thickness. The optimal thickness is 0.6 – 0.8 pm. Blued coating optimally combines corrosion resistance in low corrosive conditions with mechanical resistance to, for example, abrasion.
Using them with additional grease protection significantly improves the corrosion resistance of coating and can even improve its durability. Bluing is used for products subject to heat and thermo-chemical treatment. In contrast to galvanisation, it does not reduce mechanical parameters of the top layer. This is particularly important for products with higher mechanical properties.

List of standards
| DIN | PN | ISO | GOST | Nr Marcopol |
| ISO: ~7380 | 013.01 | |||
| ISO: ~7380 | 013.01a | |||
| ISO: ~7380 | 013.02 | |||
| ISO: ~7380 | 013.02a | |||
| ISO: 15979 | 024.01 | |||
| ISO: 15977 | 024.02 | |||
| ISO: 15980 | 024.04 | |||
| ISO: 15978 | 024.05 | |||
| ISO: 15976 | 024.06 | |||
| ISO: 15973 | 024.07 | |||
| PN: 82501 | 032.01 | |||
| PN: 82501 | 032.02 | |||
| PN-EN 10230-1 | 061.01 | |||
| PN-EN: 13964 | 051.51 – 051.58 | |||
| PN-EN 14545 | 062.01 – 062.04 | |||
| PN-EN 912 | 062.28 – 062.29 | |||
| DIN: 125 | PN: 82005 | ISO: 7089, | ||
| ISO: 7091 | GOST: 11379-68 | 014.01 | ||
| DIN: 127 | PN: 82008 | GOST: 11379-68 | 014.04 | |
| DIN: ~315 | PN: 82439 | GOST: 3032-76 | 015.10 | |
| DIN: ~316 | PN: 82436 | 011.15 | ||
| DIN: 338 | PN: 59601 | 067.01 | ||
| DIN: 338 | PN: 59601 | 067.02 | ||
| DIN: 338 | PN: 59601 | 067.03 | ||
| DIN: 340 | PN: 59601 | 067.04 | ||
| DIN: 340 | PN: 59601 | 067.05 | ||
| DIN: 436 | PN: 82010 | 014.11 | ||
| DIN: 439 | PN: 82153 | ISO: 4035 | 015.03 | |
| DIN: 440 | PN: 82019 | ISO: 7094 | 014.02 | |
| DIN: 551 | 012.05 | |||
| DIN: 553 | 012.06 | |||
| DIN: 557 | 015.31 | |||
| DIN: 562 | 015.30 | |||
| DIN: 571 | PN: 82501 | 032.03 | ||
| DIN: 580 | PN: 82472 | ISO: 3266 | 063.13 | |
| DIN: 582 | 063.14 | |||
| DIN: 603 | PN: 82406 | ISO: 8677 | 011.08 | |
| DIN: 603 | PN: 82406 | ISO: 8677 | 011.09 | |
| DIN: 605 | PN: 82402 | 011.10 | ||
| DIN: 605 | PN: 82402 | 011.11 | ||
| DIN: ~689 | ISO: ~1677-2 | 063.26 | ||
| DIN: 741 | EN 13411 | 063.15 | ||
| DIN: ~766 | 063.05 | |||
| DIN: 911 | ISO: 2936 | 049.09 | ||
| DIN: 912 | PN: 82302 | ISO: 4762 | GOST: 11738-84 | 011.06 |
| DIN: 912 | PN: 82302 | ISO: 4762 | GOST: 11738-84 | 011.07 |
| DIN: 913 | PN: 82314 | ISO: 4026 | 012.01 | |
| DIN: 914 | PN: 82315 | ISO: 4027 | 012.02 | |
| DIN: 915 | PN: 82316 | ISO: 4028 | 012.03 | |
| DIN: 916 | 012.04 | |||
| DIN: 928 | 015.20 | |||
| DIN: 929 | PN: 82169 | 015.21 | ||
| DIN: 931 | PN: 82101 | ISO: 4014 | GOST: 7798-70 | 011.02 |
| DIN: 933 | PN: 82105 | ISO: 4017 | GOST: 7798-70 | 011.01 |
| DIN: 934 | PN: 82144 | ISO: 4032 | 015.01 | |
| DIN: 960 | PN: 82101 | ISO: 8765 | 011.13 | |
| DIN: 961 | PN: 82105 | ISO: 8676 | 011.12 | |
| DIN: 965 | PN: 82208 | ISO: 7046 | 013.06 | |
| DIN: 965 | PN: 82208 | ISO: 7046 | 013.07 | |
| DIN: 966 | PN: 82212 | ISO: 7047 | 013.12 | |
| DIN: 966 | PN: 82212 | ISO: 7047 | 013.13 | |
| DIN: 967 | 013.03 – 013.05 | |||
| DIN: ~968 | 023.07 | |||
| DIN: 968 | 023.05 | |||
| DIN: 975 | 053.52 | |||
| DIN: 976 | 038.01 | |||
| DIN: 976-1 | 053.52 | |||
| DIN: 985 | PN: 82175 | ISO: 7040 | 015.04 | |
| DIN: 1480 | 063.08-063.09 | |||
| DIN: 1480 | 063.12 | |||
| DIN: 1480 | 063.28 | |||
| DIN: 1587 | PN: 82181 | 015.09 | ||
| DIN: 3050 | 063.02 | |||
| DIN: 3052 | 063.01 | |||
| DIN: 3053 | 063.02 | |||
| DIN: 3055 | 063.01 | |||
| DIN: 3060 | 063.01 – 063.02 | |||
| DIN: 3066 | 063.01 | |||
| DIN: 3127 | 049.04 | |||
| DIN: 3128 | 049.01 | |||
| DIN: 3128 | 049.02 | |||
| DIN: 5299C | 063.23 | |||
| DIN: 5299D | 063.24 | |||
| DIN: ~5685A | 063.05 | |||
| DIN: 5685A | 063.06 | |||
| DIN: 5685C | 063.07 | |||
| DIN: 6334 | PN: 82157 | 015.02 | ||
| DIN: 6379 | PN-M-82137 | 038.02 | ||
| DIN: 6797J | PN: 82023 | 014.05 | ||
| DIN: 6798A | PN: 82024 | 014.06 | ||
| DIN: 6798J | PN: 82023 | 014.05 | ||
| DIN: 6798V | PN: 82025 | 014.07 | ||
| DIN: 6899 | PN: 80247 | EN 13411 | 063.25 | |
| DIN: 6914 | PN-EN: 14399-4 | 011.33 | ||
| DIN:6915 | PN-EN: 14399-4 | 015.33 | ||
| DIN: 6916 | PN-EN: 14399-6 | 014.33 | ||
| DIN: ~6921 | ~PN-EN 1665 | |||
| ~PN-EN 1662 | ||||
| ~PN: 82247 | 011.03 | |||
| DIN: ~6921 | ~PN-EN 1665 ~PN-EN 1662 | |||
| ~PN: 82247 | 011.04 | |||
| DIN: ~6921 | ~PN-EN 1665 ~PN-EN 1662 | |||
| ~PN: 82247 | 011.05 | |||
| DIN: ~6923 | ISO: ~1661 | 015.06 | ||
| DIN: 6923 | PN: 82168 | |||
| PN-EN: 1661 | 015.05 | |||
| DIN: 6928 | ISO: 7053 | 023.02 | ||
| DIN: ~6928 | ISO: ~7053 | 023.04 | ||
| DIN: 7426 | 049.03 | |||
| DIN: 7500 | 021.02 – 021.05 | |||
| DIN: 7500 | 021.09 | |||
| DIN: 7500 CE | 021.08 | |||
| DIN: 7500 DE | 021.01 | |||
| DIN: 7500 ME | 021.06 | |||
| DIN: 7500 NE | 021.07 | |||
| DIN: 7504K | ISO: 15480 | 023.03 | ||
| DIN: 7504N | ISO: 15481 | 023.12 | ||
| DIN: 7504P | ISO: 15482 | 023.09 | ||
| DIN: 7513 | 022.02 | |||
| DIN: 7513 | 022.03 | |||
| DIN: 7513 A | 022.01 | |||
| DIN: 7516 | 022.04 | |||
| DIN: 7516 | 022.05 | |||
| DIN: 7516 AE | 022.08 | |||
| DIN: 7516 AE | 022.09 | |||
| DIN: 7516 DE | 022.06 | |||
| DIN: 7516 EE | 022.07 | |||
| DIN: ~7540 | ISO: ~1677-2 | 063.26 | ||
| DIN: 7965 | 015.14 | |||
| DIN: 7976 | PN: 83101 | ISO: 1479 | 023.01 | |
| DIN: ~7981 | PN: ~83116 | ISO: ~7049 | 023.13 | |
| DIN: 7981 | PN: 83116 | ISO: 7049 | 023.11 | |
| DIN: 7982 | PN: 83114 | ISO: 7050 | 023.08 | |
| DIN: 7983 | PN: 83115 | ISO: 7051 | 023.10 | |
| DIN: 7985 | PN: 82202 | ISO: 7045 | 013.14 | |
| DIN: 7985 | PN: 82202 | ISO: 7045 | 013.15 | |
| DIN: 7985 | PN: 82202 | ISO: 7045 | 013.18 | |
| DIN: ~7991 | ISO: ~10642 | 013.10 | ||
| DIN: ~7991 | ISO: ~10642 | 013.11 | ||
| DIN: 7991 | ISO: 10642 | 013.08 | ||
| DIN: 7991 | ISO: 10642 | 013.09 | ||
| DIN: 9021 | PN: 82030 | ISO: 7093 | 014.03 | |
| DIN: 68163 | 061.02 | |||
| DIN: 82101 | PN: 84703 | 063.22 |